Mid-Year Report on China's Urea Market in 2023
01 Analysis of China's Urea Market in the First Half of 2023
1.1 Overview of China's Urea Market
In the first half of 2023, the domestic urea market in China initially remained stable but later declined. The spot prices started a downward trend since late March, and although there was a slight rebound by the end of June, the magnitude was not significant. According to data from Feidoodoo, as of June 30, 2023, the lowest and highest values of the domestic urea small granule price index dropped by 740.71, a decrease of 26.26%.
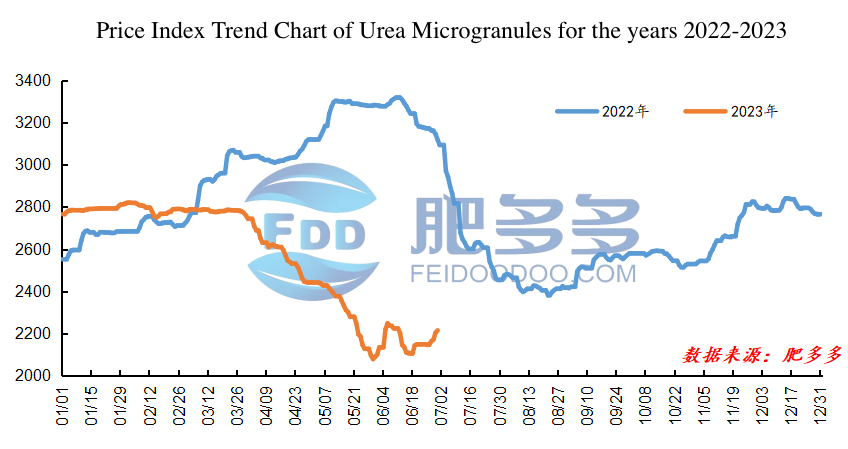
Figure 1
In the first quarter, the domestic urea market operated relatively smoothly, but experienced a decline towards the end of the quarter. After the New Year holiday, the market warmed up, and downstream demand increased slightly. However, as the supply increased, the market saw a weak upward trend and lost momentum. After the Spring Festival holiday, market players returned slowly, resulting in a supply shortage and only localized price increases for spot urea. Towards the end of the quarter, with the continued inversion of international urea prices, market players lacked confidence in the domestic urea market. The market trading gradually cooled down, and with the reduction in spring agricultural fertilization and poor performance of compound fertilizer, downstream demand weakened gradually, leading to a significant drop in urea prices.
In the second quarter, the domestic urea market entered a continuous decline mode, and there was a slight rebound in prices towards the end of the quarter. At the beginning of the quarter, with the end of green manure application in China and the gap in rice fertilizer demand in southern regions, agricultural demand continued to weaken. Urea manufacturers accumulated inventory and significantly reduced prices passively. With insufficient cost support and daily production of over 170,000 tons, companies faced negative market conditions, leading to a collapse in sentiment. Although there was some recovery in demand as the southern regions resumed fertilization after the May Day holiday, the market remained pessimistic due to the restart of low-priced urea supply from Inner Mongolia. In June, there were frequent changes in market conditions. Initially, agricultural demand concentrated on restocking, combined with the release of tender information, which provided positive market drivers, resulting in a significant increase in urea prices. However, due to high inventory pressure, the market gradually cooled down. Towards the end of the quarter, temporary shutdowns of some facilities in certain regions and a concentrated downstream restocking led to tight supply and firm spot prices.
1.2 Average Monthly Price of China's Urea Market in the First Half of 2023
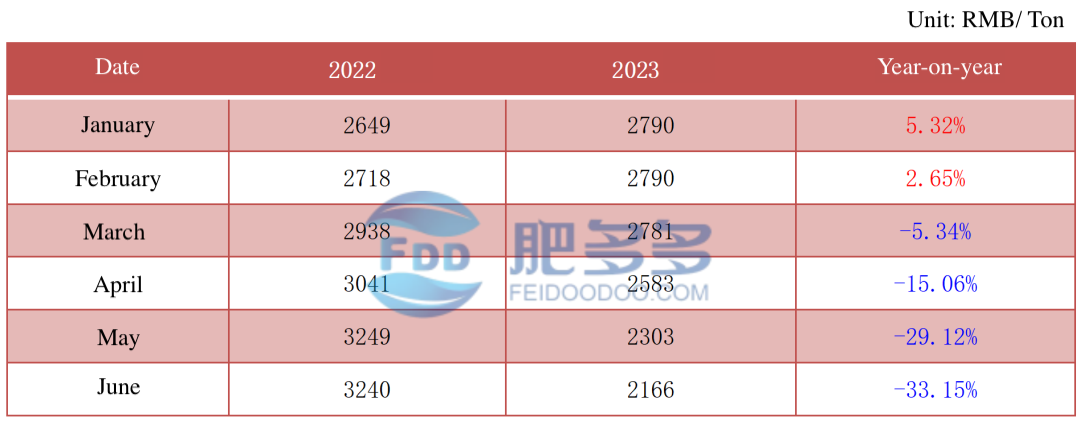
Table 1
02 Analysis of Urea Production, Operation, and Import/Export in China
2.1 Analysis of Urea Production in China in the First Half of 2023
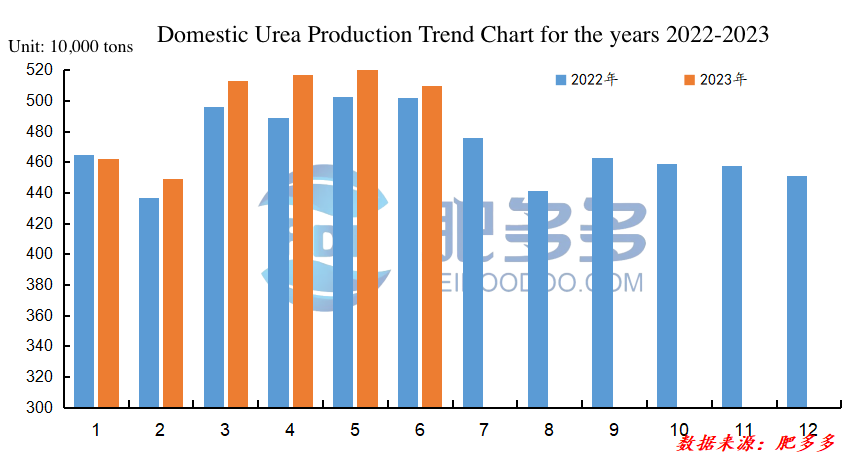
Table 2
In the first half of 2023, China's urea production reached a cumulative total of 29.7106 million tons, an increase of 0.8023 million tons compared to the same period last year, representing a year-on-year growth of 2.78%.
2.2 Analysis of Urea Industry Operation Rate in China
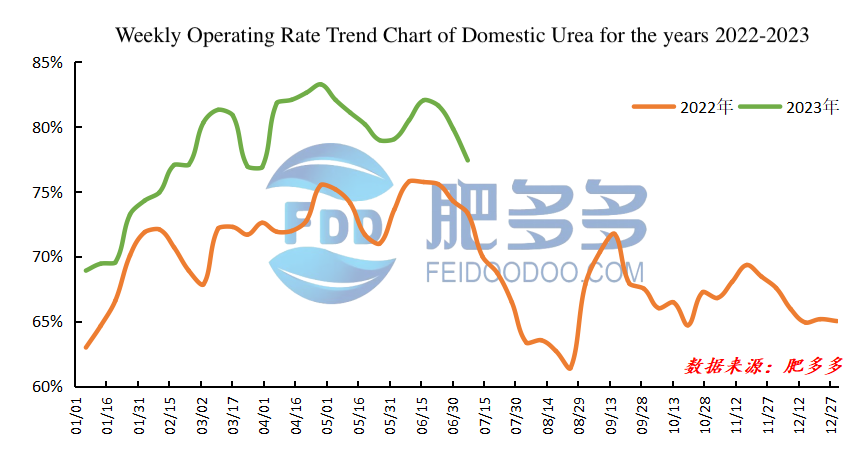
Figure 3
In the first half of 2023, the overall operation rate of the urea market in China increased and remained at a high level. The highest operation rate occurred at the end of April, while the lowest was at the beginning of January. Among them, urea manufacturers that use natural gas as raw materials had an average operating rate of 66.62%, while those using coal as raw materials had an average operating rate of 82.25%. The average operating rate for large granule plants was 67.85%, and for medium and small granule plants, it was 78.22%.
2.3 Analysis of Urea Exports in China in 2023
2.3.1 Analysis of Urea Export Volume in China in 2023
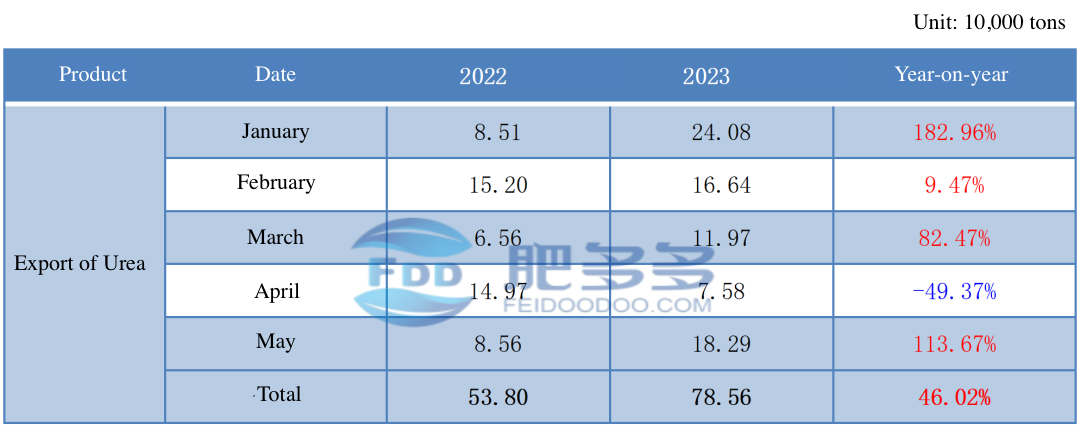
Table 2
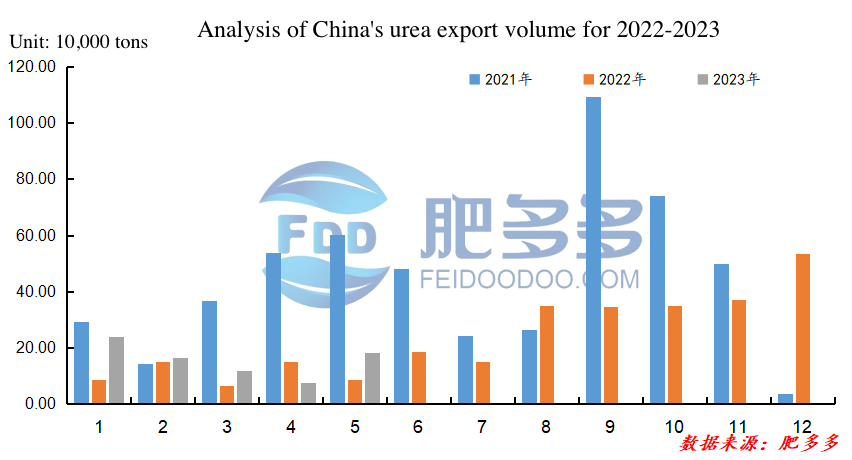
Figure 4
According to customs data, the cumulative urea export volume in China reached 538,000 tons from January to May 2023, an increase of 247,600 tons compared to the same period last year, representing a year-on-year growth of 46.02%.
2.3.2 Analysis of Urea Export Destinations in China in 2023
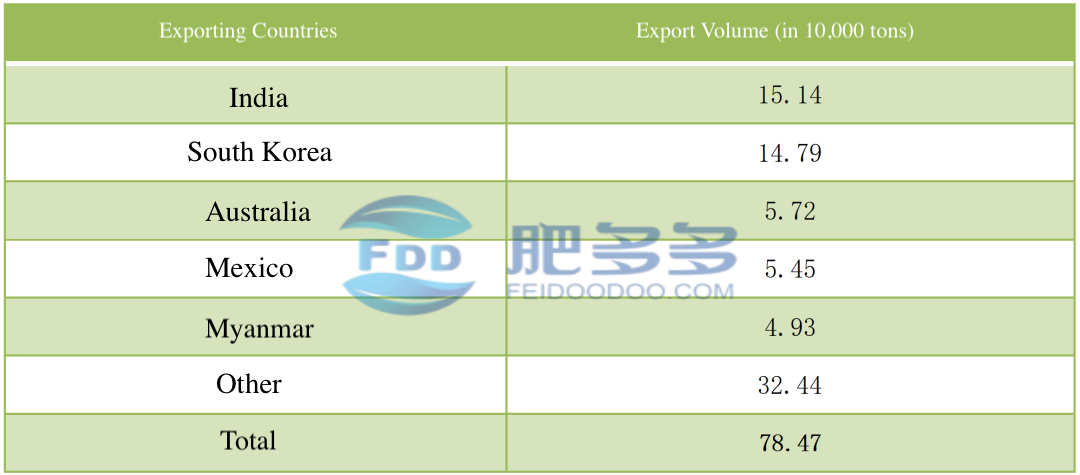
Table 3
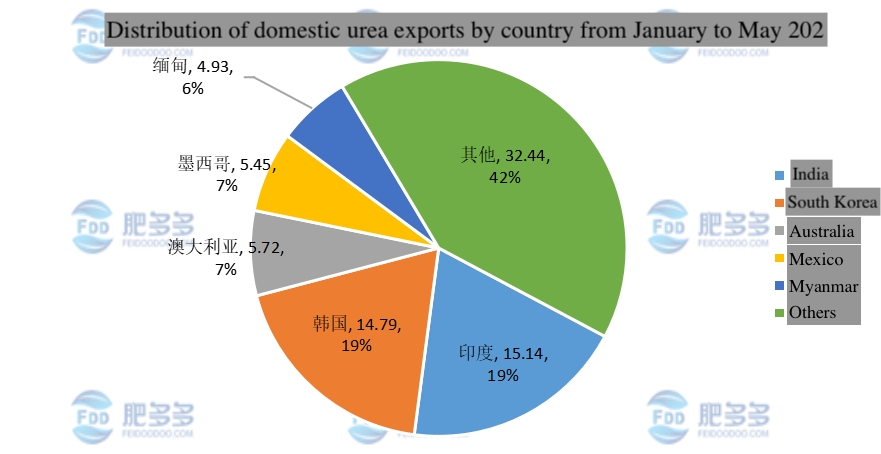
Figure 5
From January to May 2023, the top three countries in terms of urea export volume were India, South Korea, and Australia. The export volumes were 151,400 tons, 147,900 tons, and 57,200 tons, respectively.
03 Analysis of Apparent Consumption of Chinese Urea
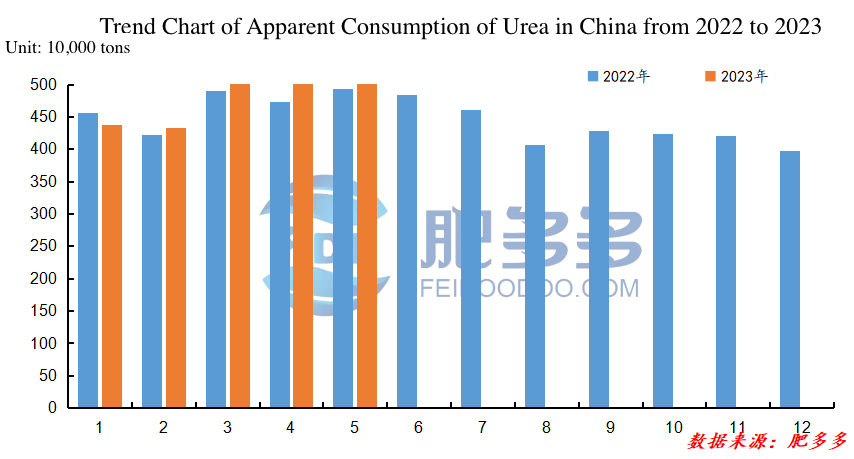
Figure 6
According to Feidoodoo data, the cumulative apparent consumption of urea in China from January to May 2023 was 23.827 million tons, an increase of 477,600 tons compared to the same period last year, representing a year-on-year increase of 2.05%.
04 Analysis of China's Urea Inventory
4.1 Trend of Large Granular Urea Port Inventory
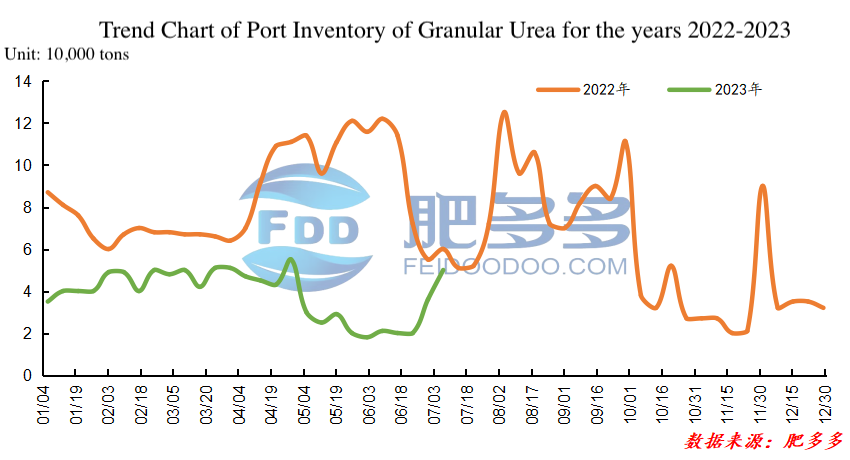
Figure 7
In the first half of 2023, the port inventory of large granular urea remained at a low level. The highest inventory was recorded at the end of April, with a peak quantity of 55,000 tons. The lowest inventory was observed at the beginning of June, with a minimum quantity of 18,000 tons.
4.2 Trend of Small Granular Urea Port Inventory
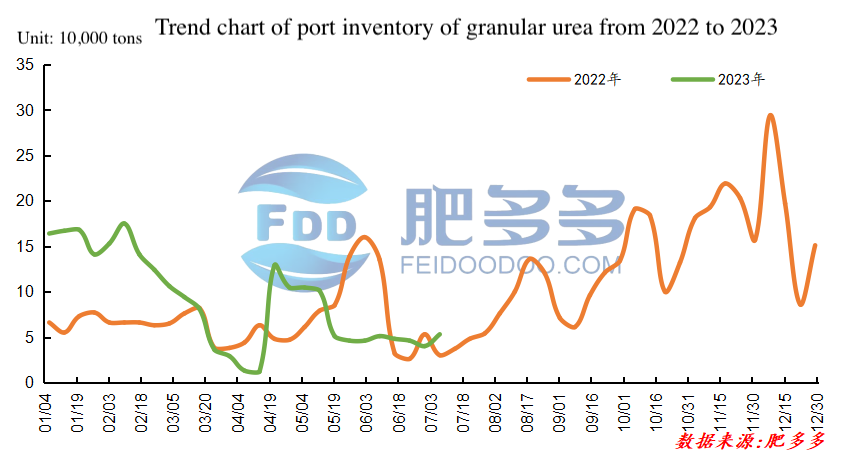
Figure 8
In the first half of 2023, the port inventory of small granular urea also remained at a low level. The highest inventory was recorded in February, with a peak quantity of 175,000 tons. The lowest inventory was observed in April, with a minimum quantity of only 12,000 tons.
4.3 Trend of Urea Enterprise Inventory
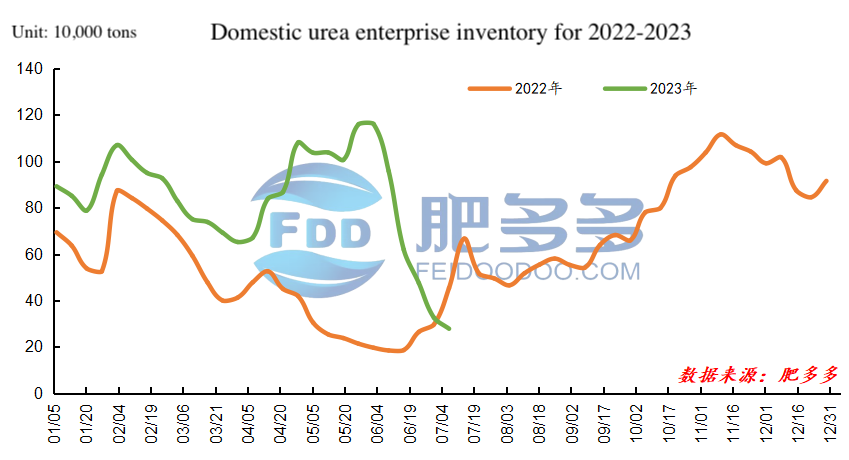
Figure 9
In the first half of 2023, the inventory of domestic urea enterprises experienced fluctuations initially but quickly accumulated inventory and then reduced rapidly after entering June. Therefore, the highest enterprise inventory was recorded at the beginning of June, with a peak quantity of 1.16 million tons. The lowest enterprise inventory was observed at the end of June, with a minimum quantity of 325,900 tons, and the current trend is still towards reduction.
05 Forecast for the Chinese Urea Market in 2023
Supply Side: Regarding synthetic urea, the international landscape continues to improve, and the stability of synthetic urea production is expected to further enhance. Based on the current situation in the urea industry, new capacity will continue to be put into operation in the second half of the year, and the supply pressure will mainly focus on coal-based urea. The coal price declined under pressure in the first half of the year, and cost stability is expected in the second half. As the cost for urea enterprises decreased and profits improved earlier, the overall supply capacity will continue to increase, and urea supply in the second half of the year is expected to be stable and sufficient.
Demand Side: In the context of food security, the total amount of urea used in agriculture is expected to remain relatively stable. The growth rate of compound fertilizer usage has declined, and seasonal factors need to be considered. Nitrogen fertilizer application may decrease in the autumn compared to the first half of the year. Due to frequent fluctuations in raw material prices, compound fertilizer enterprises face increased operational difficulties. As for industrial demand, considering the limited growth space in the real estate sector, overall industrial demand is expected to remain relatively stagnant, maintaining a procurement strategy based on demand, with occasional short-term market fluctuations.
Policy Side: In the first half of the year, sentiment in the commodity market improved in many aspects, with signs of a rebound after hitting bottom. However, the rebound was consistently weak, and concerns about foreign economic recession and the slow recovery of the domestic economy persisted. In the second half of the year, policies may continue to provide limited support but with restrained magnitude.
Overall Analysis: The supply and demand for urea are expected to remain relatively loose in the second half of the year. It is evident that high supply will continue to be the background for urea prices, and daily production may even exceed that of the first half of the year. The short-term balance of supply and demand will be influenced by seasonal variations in demand strength. The impact of exports on the urea market needs to be considered in conjunction with policies and price differentials both domestically and internationally, and it is unlikely to experience significant breakthroughs based on the trends of the first half of the year. Considering the downward shift in coal prices and increased production enthusiasm in the industry, it will be difficult for urea enterprises to replicate high profits. Short-term expectations are placed on the performance of futures and spot markets during the favorable period in September and October.
- International Fertilizer Market - Potash Giants Report First Quarter: Signs of Recovery in Potash Demand! Meanwhile, Russian Fertilizer Exports to the US Reach Annual High2743
- Phosphate Fertilizer Weekly Report: Supported by Pending Orders and Costs, Firm Prices2435
- Urea Weekly Review: Cautious Buying and Slow Follow-Up, Prices Hold Steady2532
- Urea Daily Review: Weakened Supply-Demand Support, Enterprises Lower Prices to Attract Orders2582
- Phosphate Fertilizer Daily Review: Pending Orders Support Prices, Stability in the Short Term2503





